Business Type:Manufacturer
Country/Region:China
Ddu Verified
HOT Rank


Shandong Sino Pharmaceutical Technology Co., Ltd.
We are professional supplier of Skin whitening products,Skin Rejuvenation products,Weight Less products,Peptide,Antibiotic,Analgesic,Anti-inflammatory,Vitamin,Health care products.
Business Type:Manufacturer
Country/Region:China
Ddu Verified
HOT Rank


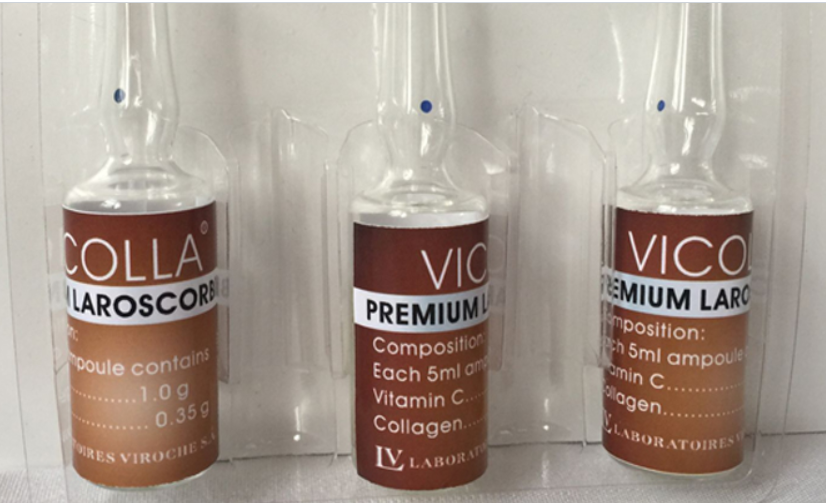
Platinum Laroscorbine
Vitamin C 10X SKIN WHITENING & LIGHTENING
Collagen ANTI-AGING PRODUCTS

1. Pharmacology
Ascorbic acid, a water-soluble vitamin, is essential for formation of collagen and intercellular material,
and therefore necessary for the development of cartilage, bone, teeth and for the healing of wounds. It is also essential for the conversion from folic acid to folinic acid, facilitates iron absorption from the gastro-intestinal tract and influences haemoglobin formation and erythrocyte maturation.
2. Indications
The prevention and treatment of scurvy, or other conditions requiring vitamin C supplementation, where the deficiency is acute or oral administration is difficult.

3. Dosage
Route of Administration: Parenteral
Adults
0.5 to 1g daily for scurvy, 200 to 500mg daily for preventative therapy.
Children
100 to 300mg daily for curative purposes, or 30mg daily for protective treatment.
Elderly
No special dosage requirements have been suggested.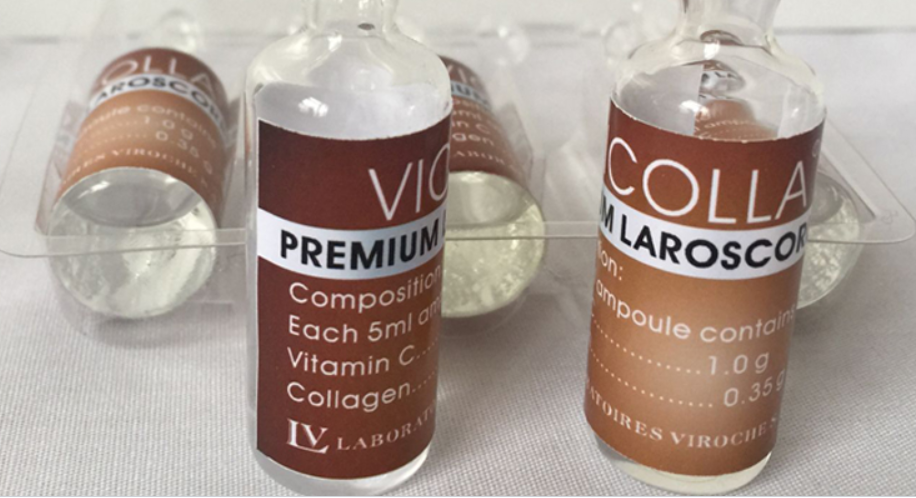
4. Contraindications
Hyperoxaluria
Special Precautions
Ascorbic acid should be given with care to patients with underlying renal due to the risk of formation of renal oxalate calculi. Tolerance may be induced in patients taking high doses.
Large doses of Ascorbic Acid have resulted in haemolysis in patients with glucose -6-phosphate dehydrogenase(G6PD)deficiency. 5. Undesirable effects
5. Undesirable effects
Large doses may cause gastrointestinal disorders including diarrhoea. Large doses may also result in hyperoxaluria and renal oxalate calculi may form if the urine becomes acidic. Doses of 600mg or more daily have a diuretic action. Induced tolerance with prolonged use of large doses can result in symptoms of deficiency when intake is reduced to normal.
